Q: What makes a recumbent bike a magnetic recumbent bike?
A: The use of magnetic eddy currents in the braking mechanism (ECB).
A magnetic eddy current brake or “magnetic ECB” capitalizes on the magnetic field anomaly called an “eddy current.”
Much like the way eddy currents form in water, the eddy currents around a magnetic field create their own swirling effects and their own magnetic field. Those eddy currents can be used to create a braking effect by using the resistance of these eddy currents to oppose the rotational direction of the flywheel on the recumbent exercise bike.
The XTerra Fitness SB 540r Indoor Stationary Magnetic Recumbent Exercise Fitness Bike
I’m not an electrical engineer so I thought perhaps a diagram might help illustrate how a recumbent exercise bike becomes a magnetic resistance recumbent exercise bike using magnetic ECB for resistance.
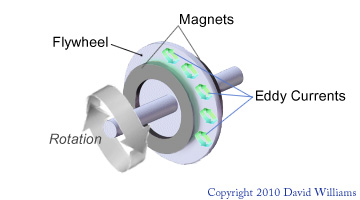
The eddy currents that are generated are perpendicular to the flywheel’s direction of travel. In the case of magnetic eddy current brakes, the metal flywheel is exposed to a magnetic field from an electromagnet, creating eddy currents in the flywheel. The eddy currents meet resistance as charges flow through the flywheel, and this acts to slow down the rotation of the flywheel. Interestingly, the faster the flywheel is spinning (RPMs), the stronger the effect, meaning that as the bike slows the braking (resistance) force is reduced, producing a very smooth ‘braking’ action which results in extremely smooth transitions between resistance levels.
Let’s use the XTerra SB540R Stationary Recumbent Bike (which has a larger flywheel) as an example. When you use a preselected program or set up your own user program – you can specify the resistance levels for each segment of the fitness program.
So, let’s say you use the control panel and choose to begin your workout with a resistance level of 5 for the first segment, 9 for the second segment and 16 for the third segment thru the sixth segment and then step the resistance back down to warm down; instead of feeling abrupt and rapid changes in the transition between the different resistance levels – you will feel a gradual change in the resistance level that is very comfortable to adapt to.
Knowing how each type of resistance mechanism works will help you make an informed decision before you make a purchase.
Magnetic ECB resistance mechanisms are becoming increasingly popular. In the SB540R magnetic recumbent bike, the magnetic currents track the resistance level so that you can make the necessary adjustments depending on your preferred level of intensity. A magnetic resistance bike offer more because they are easier to adjust, have a more sophisticated resistance level, smoother to use and are quieter than other types of resistance mechanisms.
Direct Tension and Direct Friction resistance mechanisms are decreasing in popularity and actually harder to find. They are awkward, noisy and use actual friction of moving parts to adjust the tension level and they required the rider to make manual adjustments.
Wind Resistance mechanisms were very popular before the turn of the century but they too are decreasing in popularity. Air resistance bikes work by using a fan blade to create resistance.
The XTerra Fitness SB540R has a more heavily weighted flywheel resistance and an extremely smooth belt driven feature – Very Quiet to ride – very easy to adjust with a few touches on the control panel. Smooth transitions, quiet and comfortable, easy to adjust on the fly, affordable, reliable and low-maintenance recumbent cycling in the comfort of your own home.
Proper Seat Adjustment
With your heel on the pedal your leg should be straight or a bit over extended. Then you pedal with the ball of your foot on the pedal and there is a bit of flex left in your knee.
- Pain in the front of your knee usually means too much leg bend.
- Pain in the back (rare) usually means to little bend.
 Bicycle Man
Bicycle Man 